New human species identified from Kenya fossils
Source: bbc.co.uk

Researchers studying fossils from northern Kenya have identified a new species of human that lived two million years ago.
The discoveries suggests that at least three distinct species of humans co-existed in Africa.
The research adds to a growing body of evidence that runs counter to the popular perception that there was a linear evolution from early primates to modern humans.
The research has been published in the journal Nature.
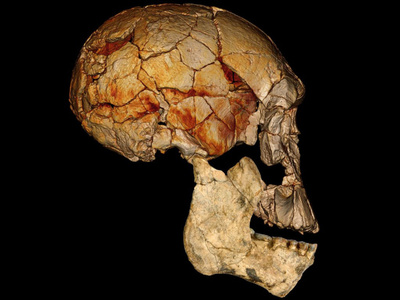
Anthropologists have discovered three human fossils that are between 1.78 and 1.95 million years old. The specimens are of a face and two jawbones with teeth.
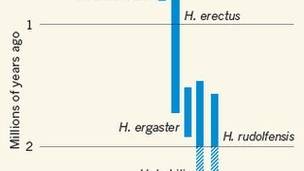
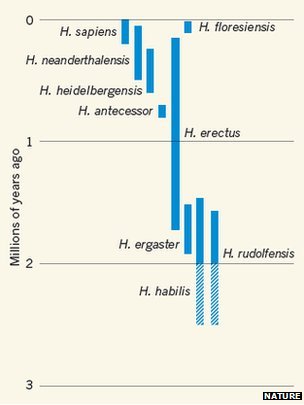
The finds back the view that a skull found in 1972 is of a separate species of human, known as Homo rudolfensis. The skull was markedly different to any others from that time. It had a relatively large brain and long flat face.
But for 40 years the skull was the only example of the creature and so it was impossible to say for sure whether the individual was an unusual specimen or a member of a new species.
With the discovery of the three new fossils researchers can say with more certainty that H.rudolfensis really was a separate type of human that existed around two million years ago alongside other species of humans.
For a long time the oldest known human ancestor was thought to be a primitive species, dating back 1.8 million years ago called Homo erectus. They had small heads, prominent brows and stood upright.
A new species of human: One of several co-existing in Africa two million years ago
But 50 years ago, researchers discovered an even older and more primitive species of human called Homo habilis that may have coexisted with H. erectus. Now it seems H. rudolfensis was around too and raises the distinct possibility that many other species of human also existed at the time.
This find is the latest in a growing body of evidence that challenges the view that our species evolved in a smooth linear progression from our primate ancestors.
 Instead, according to Dr Meave Leakey of the Turkana Basin Institute in Nairobi, who led the research the find shows that there was a diversity early on in the evolution of our species.
Instead, according to Dr Meave Leakey of the Turkana Basin Institute in Nairobi, who led the research the find shows that there was a diversity early on in the evolution of our species."Our past was a diverse past," she told BBC News, "our species was evolving in the same way that other species of animals evolved. There was nothing unique about us until we began to make sophisticated stone tools."
In other groups of animals many different species evolve, each with new traits, such as plumage, or webbed feet. If the new trait is better suited to the environment then the new species thrives, if not it becomes extinct.
According to Professor Chris Stringer of the Natural History Museum in London, fossil evidence is increasingly suggesting that human evolution followed the same pattern.
"Humans seem to have been evolving in different ways in different regions. It was almost as if nature was developing different human prototypes with different attributes, only one of which, an ancestor of our species, was ultimately successful in evolutionary terms," he said.
According to Dr Leakey, the growing body of evidence to suggest that humans evolved in the same way as other animals shows that "evolution really does work".
"It leads to amazing adaptions and amazing species and we are one of them," she said.
Article from: bbc.co.uk
New Human Haplogroup Announcements Question the ’Out of Africa’ Hypothesis
The newly discovered face and lower-jaw fossils, uncovered within a radius of just more than 6 miles (10 kilometers) from where KNM-ER 1470 was unearthed, now suggest that KNM-ER 1470 and the novel finds are indeed members of a distinct species of early Homo that stands out from others with its uniquely built face.
"It had very flat facial features — you could draw a straight line from its eye socket to where its incisor teeth would be," researcher Fred Spoor at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, told LiveScience. "This shows east Africa about 2 million years ago was quite a crowded place with many diverse species of early Homo," Spoor said.
The environment was more verdant back then than it is today, with a larger lake. "There was plenty of opportunities ecologically to accommodate more than one hominid species," Spoor said.
Other researchers suggest these new fossils are not enough evidence of a new human species. However, "these are really distinctive shape profiles — it really shows something completely different," Leakey said. "I feel pretty confident that we’re not just dealing with variation in one species."
In principle, researchers might be able to reconstruct what this new species might have eaten by looking at its teeth and jaws. "The incisors are really rather small compared to what you’d find in other early Homo," Spoor said. "In the back of the mouth, the teeth are large, telling us a lot of food processing was going on there ... it may be possible it ate more tough, plantlike foods than meat."
Source
The "Hobbit" Of Flores
Also tune into Red Ice Radio:
Joseph Farrell - Hour 1 - Yahweh The Two-Faced God [Farrell questions the "Out of Africa" theory and the origin of Europeoids (Caucasoid) in light of new DNA genealogy]
Lloyd Pye - The Starchild Skull & DNA Revelations
Lloyd Pye - Starchild Skull DNA, Disclosure & Directed Panspermia
Barbara Hand Clow - Beyond Trauma & Acceleration of Consciousness
Lloyd Pye - Hominoids
Bob Curran - Dark Fairies, Folklore, Spirits & Creatures
Jeff Hilling - Hour 1 - The Patterson Bigfoot Film