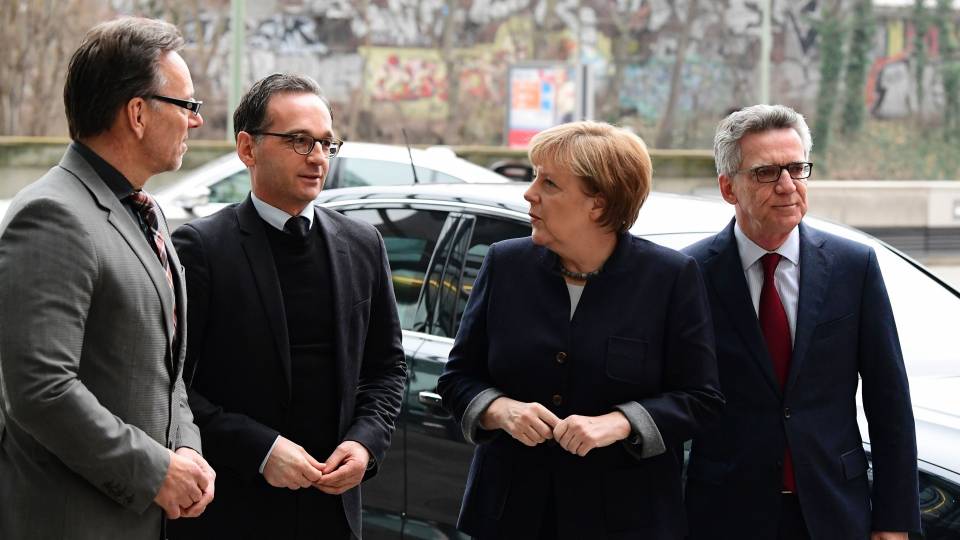
Germany Raids Homes of 36 People Accused of Hateful Postings Over Social Media
In a coordinated campaign across 14 states, the German police on Tuesday raided the homes of 36 people accused of hateful postings over social media, including threats, coercion and incitement to racism.
Most of the raids concerned politically motivated right-wing incitement, according to the Federal Criminal Police Office, whose officers conducted home searches and interrogations. But the raids also targeted two people accused of left-wing extremist content, as well as one person accused of making threats or harassment based on someone’s sexual orientation.
“The still high incidence of punishable hate posting shows a need for police action,” Holger Münch, president of the Federal Criminal Police Office, said in a statement. “Our free society must not allow a climate of fear, threat, criminal violence and violence either on the street or on the internet.”
In Communist Germany! Raids on people who speak out against their destruction https://t.co/YFXlypFoT4
— Lana (@LanaLokteff) June 30, 2017
The raids come as Germans are debating the draft of a new social media law aimed at cracking down on hate speech, a measure that an array of experts said was unconstitutional at a parliamentary hearing on Monday.
The measure, championed by Justice Minister Heiko Maas for passage this month, would fine Facebook, Twitter and other outlets up to $53 million (50 million euros) if they failed to remove hate speech and other forms of illegal content.
Under German law, social media users are subject to a range of punishments for posting illegal material, including a prison sentence of up to five years for inciting racial hatred.
Under the draft statute, networks must offer a readily available complaint process for posts that may amount to threats, hate speech, defamation, or incitement to commit a crime, among other offenses.
Social media outlets would have 24 hours to delete “obviously criminal content” and a week to decide on more ambiguous cases. The law, approved by Germany’s cabinet in April, would be enforced with fines of up to $53 million.
According to a recent government study, Facebook deleted just 39 percent of illegal hate speech within 24 hours in January and February, despite signing a code of conduct in 2015 pledging to meet this standard. Twitter deleted just 1 percent.
“We are disappointed by the results,” Klaus Gorny, a Facebook spokesman, said in a statement this year regarding the study. “We have clear rules against hate speech and work hard to keep it off our platform.”
But even as Mr. Maas and his allies advocate parliamentary approval, eight of 10 experts who testified at a parliamentary hearing on Monday said the law would not withstand constitutional scrutiny.
Bernd Holznagel, a professor at the University of Münster and one of the participating experts, pointed to two constitutional violations related to freedom of speech: the statute gives companies incentives to remove content, and it lacks a procedure for users to appeal removals.
“Our constitutional court will not allow such a statute,” Mr. Holznagel said. “I think they would crush it,” he continued. “The statute sets up incentives to take out content if there is any doubt, so there is an incentive to erase speech, and that cannot be upheld.
“The second point is the other side of the coin, because if there is just an incentive to remove, what about the rights of the speaker who posts the content?” he added.
Other experts expressed concerns that the law would vest private companies with too much policing responsibility.
Christian Mihr, another panelist and managing director of Reporters Without Borders, said the law would unwisely transfer authority from Germany’s justice system to companies like Facebook and Twitter.
According to Mr. Mihr, Germany’s current instruments for persecuting hate speech, as demonstrated by Tuesday’s raids, are working. “The raid shows that we don’t need this law because we have already instruments for persecuting such crimes,” he said.