The Nebra Sky Disc - Ancient European Map of the Stars
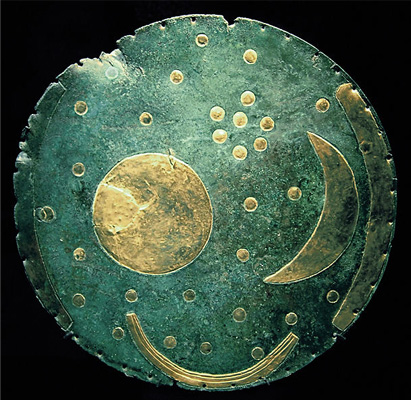
In 1999 a mysterious disc was unearthed in Nebra, Germany, and it fascinated researchers with it’s strange golden markings. The weathered and dented disc, unearthed by treasure hunters, had a blue-green patina, and was embellished with golden symbols.
Until 2006, the Sky Disc of Nebra was considered a hoax, an enigma to the archaeological world - but its meaning was deciphered, and it changed history.
The disc’s golden pieces demonstrate astronomical alignments, with a sun, moon, and stars, all found to depict the oldest known representation of the heavens.
In an article from 2006 about the discovery, DW.com described the "gold-leaf appliqués representing the sun, the moon, and the stars is the oldest visual representation of the cosmos known to date. A cluster of seven dots has previously been interpreted as the Pleiades constellation as it appeared 3,600 years ago. "
The disc it is known as an authentic and priceless Bronze Age religious and astronomical artifact. It is said to have unlocked the secrets of European history and civilization.
THE NEBRA SKY DISC - Ancient European Map of... by AveEuropa
Bronze Age Sky Disc Deciphered
From: DW.de
A group of German scientists has deciphered the meaning of one of the most spectacular archeological discoveries in recent years: The mystery-shrouded sky disc of Nebra was used as an advanced astronomical clock.
The purpose of the 3,600 year-old sky disc of Nebra, which caused a world-wide sensation when it was brought to the attention of the German public in 2002, is no longer a matter of speculation.
A group of German scholars who studied this archaeological gem has discovered evidence which suggests that the disc was used as a complex astronomical clock for the harmonization of solar and lunar calendars.
"This is a clear expansion of what we knew about the meaning and function of the sky disc," said archeologist Harald Meller.
A thirteenth month?
Unlike the solar calendar, which indicates the position of the earth as it revolves around the sun, the lunar calendar is based on the phases of the moon. A lunar year is eleven days shorter than the solar year because 12 synodic months, or 12 returns of the moon to the new phase, take only 354 days.
The sky disc of Nebra was used to determine if and when a thirteenth month -- the so-called intercalary month -- should be added to a lunar year to keep the lunar calendar in sync with the seasons.
"The functioning of this clock was probably known to a very small group of people," Meller said.
[...]
From Saxony-Anhalt to Babylon
 The sky disc of Nebra was found near Europe’s oldest observatory in Goseck |
"I wanted to explain the thickness of the crescent on the sky disc of Nebra because it is not a new moon phase," said Hamburg astronomer Ralph Hansen.
In his quest to explain why the Nebra astronomers created a sky map with a four or five days old moon on it, Hansen consulted the "Mul-Apin" collection of Babylonian documents from the 7th and 6th centuries B.C.
These cuneiform writings represent, according to Hansen, a compendium of "astronomic knowledge from the earliest times." They also contain a calculation rule for the crescent that looks strikingly similar to the one from Nebra.
According to the ancient Babylonian rule, a thirteenth month should only be added to the lunar calendar only when one sees the constellation of the moon and the Pleiades exactly as they appear on the Nebra sky disc.
Read the full article at: dw.de






















